Photo: Live Pixel
Have you had a friend or teammate who has had a groin injury? Have they seen physiotherapists, chiropractors or other health practitioners who have all given them different diagnosis?
This is a common problem in groin pain and not only is it frustrating for the individual, but it makes the rehabilitation of the injury borderline impossible. This problem is not unique to Australia, it is a problem all around the world.
Luckily we have some excellent physiotherapists, sports doctors and orthopaedic surgeons in this world of ours who want to put an end to this.
The Doha consensus statement on groin pain was developed in 2014 to ensure this is no longer a problem. This consensus statement enables all clinicians dealing with groin pain to speak a common language.
I think it is important to talk about what we shouldn’t call the various types of groin pain, the list is lengthy:
- Adductor and iliopsoas tendinitis or tendinopathy
- Athletic groin pain or athletic pubalgia
- Bio-mechanical groin overload
- Gilmore’s groin
- Groin disruption
- Osteitis pubis,
- Sports groin or sportsman’s groin
- Sports hernia or sportsman’s hernia
So what can we use? This diagram (figure 1) is a nice graphic of the terms that should be used when talking about groin pain
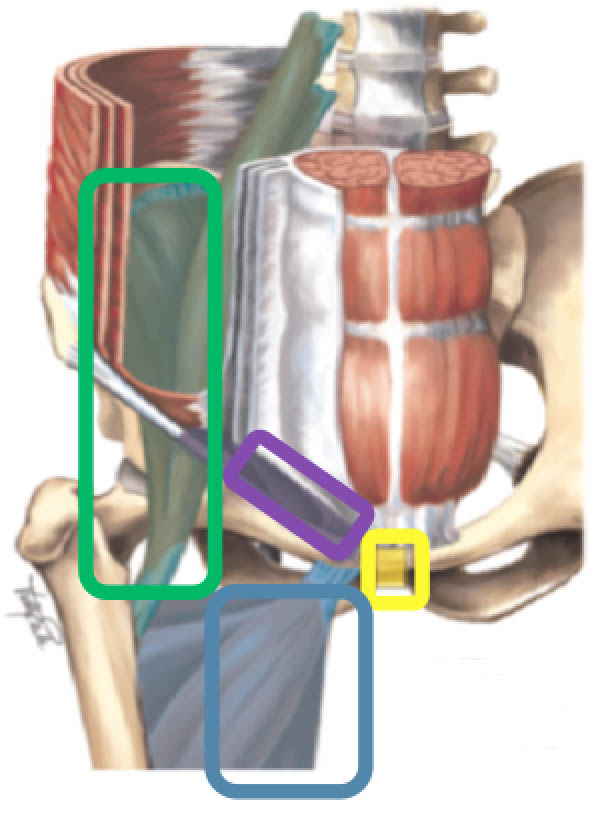
Fig. 1. Defined locations and definitions for groin pain.[1]
What are the different types of groin pain?
Adductor related groin pain
Adductor related groin pain can be considered as groin pain that exists around the adductor muscles or their tendon. This is the most common form of groin pain seen in soccer players.
How to diagnose it?
Pain on the tendon
Pain with squeezing the groin muscles (below)
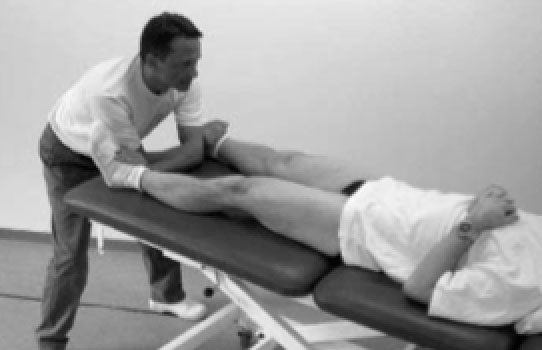
Fig. 2. Groin squeeze against resistance.[2]
Iliopsoas related groin pain
Iliopsoas related groin pain can be considered as groin pain that exists around the hip flexor muscles or their tendon. This is a common form of groin pain seen in kicking sports.
How to diagnose it?
Pain on stretching the hip flexors
Pain with using the hip flexor muscles to bend the hip (below)
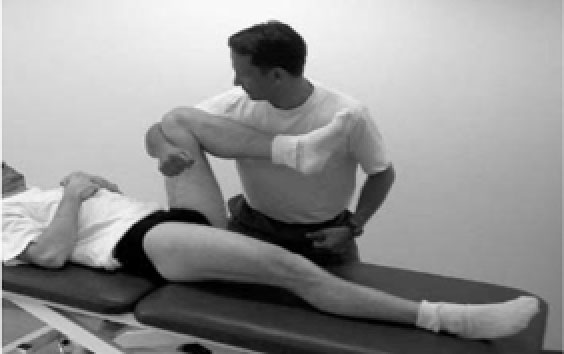
Fig. 3. Hip flexion against resistance[2]
Inguinal related groin pain
Inguinal related groin pain can be considered as groin pain that exists within or around the inguinal canal. This is a common form of groin pain seen in kicking sports.
How to diagnose it?
Pain around the inguinal canal or pain with pressure over the area
Pain with resisted sit up or coughing (below)
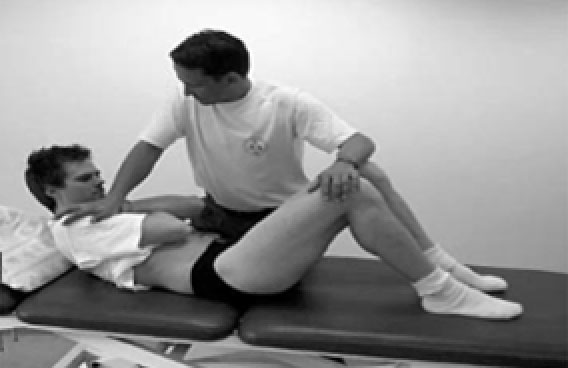
Fig. 4. Resisted sit up[2]
Pubic Related Groin Pain
Pubic related groin pain can be considered as groin pain that is located around or with pressure over the pubic bone (figure 5).
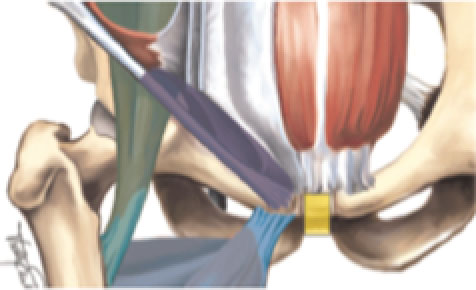
Fig. 5. Defined locations and definitions for groin pain[1]
The Doha groin consensus statement has been a giant step forward for health professionals treating people with groin pain. It provide us with a common language to speak and will result better outcomes for those dealing with this troublesome condition.

 A former Premiership winning player at South Hobart FC, Josh is a physiotherapist with extensive experience dealing with hip and groin pain in football players. He is currently undertaking his PhD, looking at hip and groin pain in soccer players. More information about his research can be found at http://semrc.blogs.latrobe.edu.au/force-trial/
A former Premiership winning player at South Hobart FC, Josh is a physiotherapist with extensive experience dealing with hip and groin pain in football players. He is currently undertaking his PhD, looking at hip and groin pain in soccer players. More information about his research can be found at http://semrc.blogs.latrobe.edu.au/force-trial/
References
1. “Doha agreement meeting on terminology and definitions on terminology and definitions in groin pain in athletes” by Weir, A., Brukner, P., Delahunt, E., Ekstrand, J., Griffin, D., Khan, K. M., . . . Holmich, P. 2015. British Journal of Sports Medicine 49(12), 768-774
2. “Clinical examination of athletes with groin pain; an intraobserver and interobserver reliability study” by Holmich, P., Holmich, L., Bierg, A., 2004, British Journal of Sports Medicine 38

